Transmedia Learning: Engaging Students in Environmental Issues

Understanding Transmedia Learning and Its Benefits
Transmedia learning is a dynamic approach that combines multiple media platforms to enhance educational experiences. Imagine a classroom where students engage with a story across books, videos, and interactive games. This method not only captures their attention but also allows for deeper understanding and retention of information. By weaving narratives through various formats, educators can create a rich tapestry of learning that resonates with diverse learners.
Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.
One of the key benefits of transmedia learning is its ability to foster critical thinking. Students are encouraged to analyze content from different perspectives, making connections that might otherwise go unnoticed. For instance, a documentary on climate change can be complemented by a podcast featuring interviews with environmental activists. This multifaceted approach helps students grasp complex issues and encourages them to question and explore further.
Additionally, transmedia learning promotes collaboration among students. As they navigate different platforms, they can share insights, discuss concepts, and work together on projects. This sense of community not only enhances learning but also cultivates a shared responsibility for the environment, empowering students to become advocates for change.
The Role of Storytelling in Environmental Education
Storytelling is a powerful tool in transmedia learning, especially when it comes to environmental education. Narratives can evoke emotions and create a personal connection to environmental issues, making them more relatable. For example, a story about a community impacted by pollution can resonate with students, prompting them to think critically about their own surroundings and actions.
Furthermore, stories can highlight solutions and inspire action. By featuring characters who take steps towards sustainability, educators can motivate students to envision themselves as agents of change. This approach not only educates but also empowers, as students see that they, too, can make a difference in their communities.
Transmedia Learning Enhances Education
Transmedia learning utilizes multiple media platforms to create engaging educational experiences that cater to diverse learning styles.
Incorporating diverse voices into storytelling also enriches the learning experience. By showcasing perspectives from various cultures and backgrounds, students gain a holistic view of environmental issues. This inclusivity fosters empathy and understanding, encouraging students to appreciate the interconnectedness of global challenges.
Using Multimedia Tools for Environmental Exploration
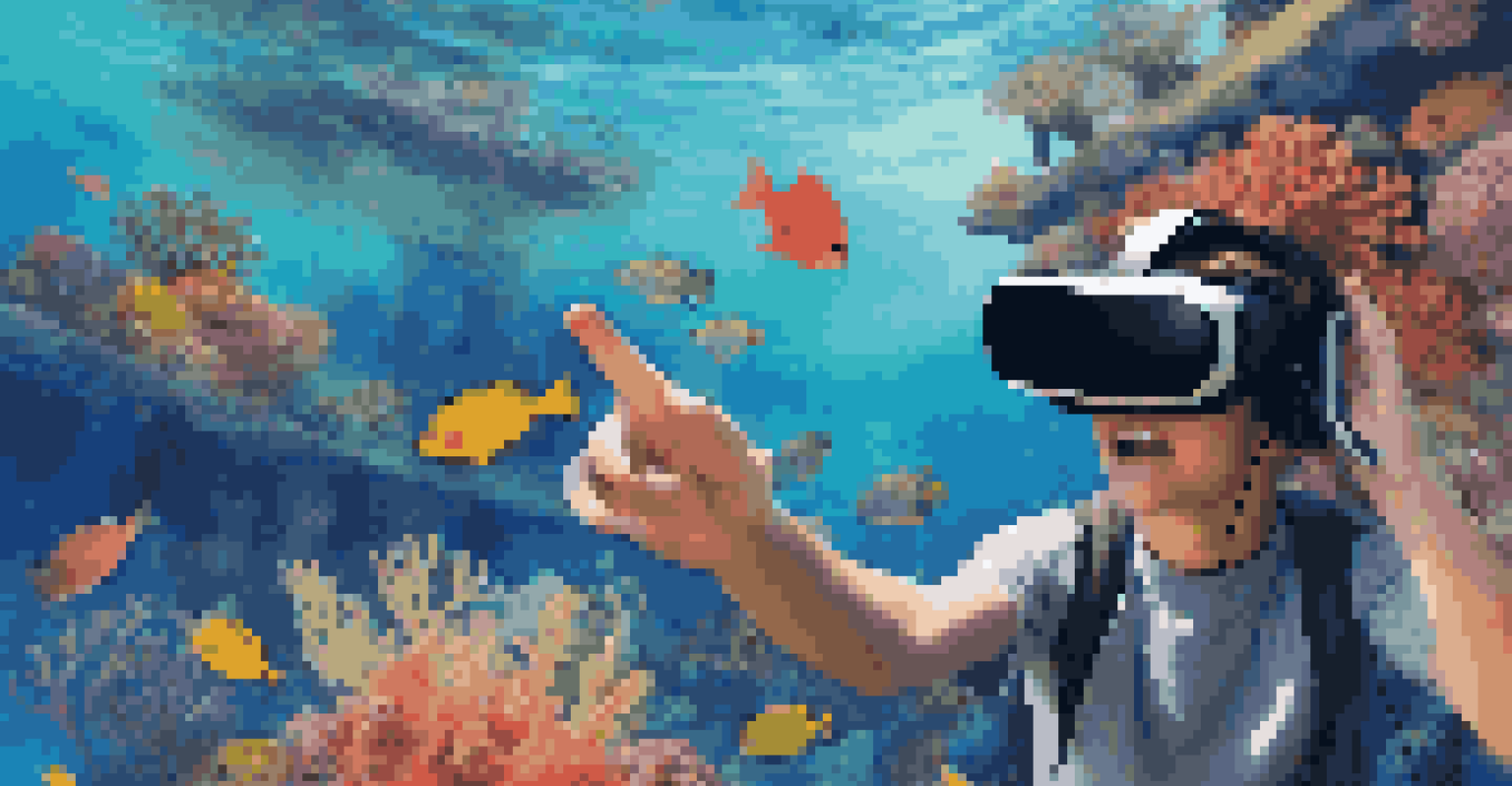
Multimedia tools are essential in transmedia learning, providing varied ways for students to engage with environmental content. From interactive maps to virtual reality experiences, these tools can transport students into ecosystems they may never visit. Imagine exploring a coral reef through a VR headset while learning about its challenges and conservation efforts.
The greatest threat to our planet is the belief that someone else will save it.
These tools also allow for personalized learning experiences. Students can choose how they want to engage with the material, catering to their interests and learning styles. For instance, some may prefer watching a documentary, while others might enjoy participating in an online forum discussing environmental policies.
Moreover, multimedia tools can enhance collaboration and creativity. Students can create their own content, such as videos or podcasts, to share their insights on environmental issues. This not only reinforces their understanding but also encourages them to express their voices in meaningful ways.
Creating Interactive Learning Experiences
Interactive learning experiences are a hallmark of transmedia education. By incorporating activities like role-playing or simulations, educators can immerse students in real-world environmental scenarios. For example, students might simulate a town hall meeting where they debate local climate policies, allowing them to experience the complexities of decision-making.
These interactive elements foster engagement and retention. When students actively participate rather than passively consume information, they are more likely to remember what they've learned. This hands-on approach can make even challenging topics, such as ecological sustainability, feel approachable and relevant.
Storytelling Drives Environmental Awareness
Effective storytelling in environmental education fosters emotional connections, inspiring students to become advocates for change.
Additionally, interactive experiences promote teamwork and communication skills. Students learn to collaborate, share ideas, and respectfully disagree, all while working towards a common goal. This not only prepares them for future environmental advocacy but also for collaborative efforts in any field.
Fostering Critical Environmental Awareness Through Transmedia
Transmedia learning helps cultivate a critical awareness of environmental issues among students. By engaging with diverse media, students encounter various viewpoints and data, prompting them to question the status quo. This critical lens is vital in today’s world, where misinformation can easily spread and shape public opinion.
Educators can guide students in analyzing sources and recognizing biases, enhancing their ability to discern credible information. For instance, comparing articles from different outlets on climate change can spark discussions about media representation and accountability. This analytical approach empowers students to become informed citizens who can advocate for change.
Moreover, fostering critical awareness encourages a sense of agency. When students understand the complexities of environmental issues, they are more likely to take action, whether through personal choices or community involvement. This proactive mindset is essential for nurturing a generation committed to sustainability.
Integrating Community Involvement in Learning
Community involvement is a crucial aspect of transmedia learning, especially for environmental education. By connecting classroom lessons to real-world initiatives, students can see the tangible impact of their learning. For example, partnering with local environmental organizations for clean-up events can turn theoretical knowledge into practical action.
These partnerships also enrich the educational experience by providing students with mentorship and guidance from community leaders. Engaging with experts can inspire students and offer them a broader perspective on environmental issues. This connection underscores the importance of collaboration between schools and communities in addressing environmental challenges.
Community Involvement Strengthens Learning
Engaging with local environmental initiatives allows students to see the real-world impact of their education, fostering a sense of responsibility.
Additionally, community involvement fosters a sense of belonging and responsibility. When students actively participate in local environmental efforts, they develop a personal stake in the health of their surroundings. This sense of ownership can motivate them to pursue long-term commitments to sustainability and advocacy.
Assessing the Impact of Transmedia Learning
Assessing the impact of transmedia learning on student engagement and understanding is vital for educators. Traditional assessments may not capture the depth of learning that occurs through this multifaceted approach. Instead, educators can utilize reflective journals, portfolios, or presentations to gauge student progress and insights.
Moreover, feedback from students can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of transmedia methods. Understanding what resonates with students helps educators refine their approaches and create more engaging content. Surveys or focus groups can be effective tools for gathering these insights.

Ultimately, assessing the impact of transmedia learning is not just about measuring knowledge; it's about understanding how it transforms students' perspectives on environmental issues. By evaluating both cognitive and emotional responses, educators can ensure that their teaching methods foster a genuine connection to the environment.