The Intersection of VR Technology and Educational Psychology
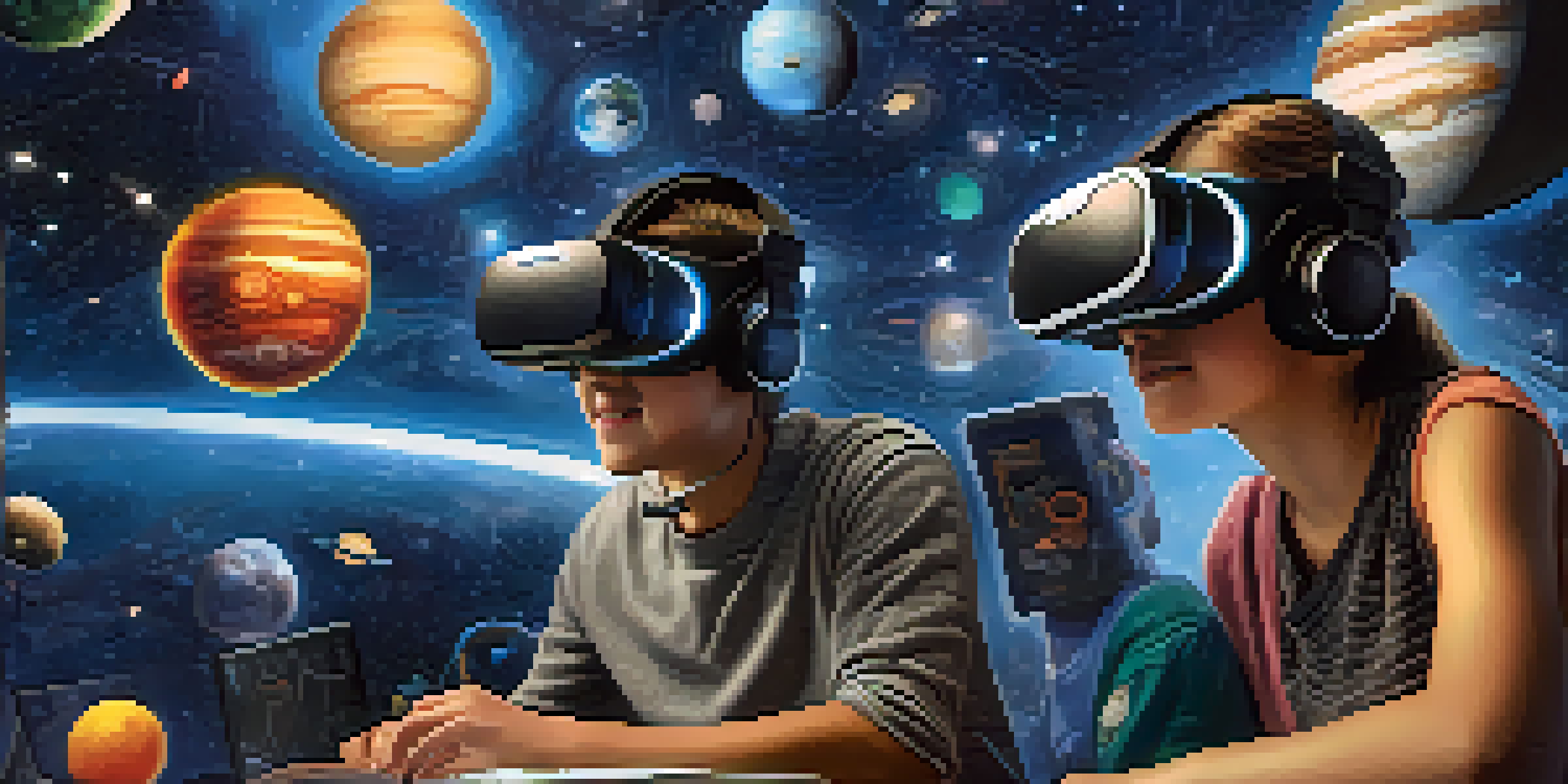

Understanding VR Technology in Education
Virtual Reality (VR) technology immerses users in a 3D environment, allowing them to interact with the space in a way that feels real. In education, this means students can explore complex subjects, from historical events to scientific phenomena, in a hands-on manner. By engaging multiple senses, VR can create memorable learning experiences that traditional methods often lack.
Virtual reality is not just a new technology; it is a new medium of expression and a new way of learning.
For example, imagine learning about the solar system not just through textbook illustrations but by actually 'visiting' each planet. Students can observe the characteristics of each celestial body up close, fostering deeper understanding. This immersive approach not only captures attention but also encourages students to explore concepts actively, making learning more effective.
Moreover, the adaptability of VR means it can cater to various learning styles, whether visual, auditory, or kinesthetic. As a result, educators can tailor lessons to fit individual needs, promoting inclusivity and better engagement across diverse classrooms.
The Role of Educational Psychology in VR Design
Educational psychology focuses on how students learn and the psychological factors that influence their educational experience. When designing VR educational tools, understanding these principles is crucial to creating effective learning environments. For instance, incorporating elements that promote motivation and reduce anxiety can lead to more successful learning outcomes.
For example, VR simulations that provide immediate feedback can enhance motivation by allowing students to see the consequences of their actions in real-time. This aligns with psychological theories of reinforcement, where positive outcomes encourage repeated engagement. By ensuring that VR experiences are both challenging and achievable, educators can foster a growth mindset among learners.
VR Enhances Immersive Learning
Virtual Reality provides students with hands-on, immersive experiences that deepen understanding of complex subjects.
Furthermore, leveraging concepts like cognitive load theory can help in VR design, ensuring that information is presented in a digestible manner. By balancing the amount of new information with the user's processing capacity, VR can facilitate deeper learning without overwhelming students.
Enhancing Engagement Through Immersive Experiences
One of the most significant advantages of VR in education is its ability to boost student engagement. Immersive environments capture attention and stimulate curiosity, making learning feel more like an adventure than a chore. Through experiences that transport students to different worlds, they can develop a passion for subjects that might otherwise seem tedious.
The best way to predict the future is to create it.
For instance, students studying anatomy can 'walk' through a human body, observing organs and systems in a way that static images simply can't replicate. This level of engagement can lead to improved retention of information, as students are more likely to remember what they actively explore rather than what they're passively told.
Moreover, immersive experiences can facilitate collaborative learning, as students can interact with both the content and each other in real-time. Group activities in virtual settings encourage teamwork and communication, essential skills in today’s interconnected world.
Overcoming Learning Barriers with VR
VR technology has the potential to break down various barriers to learning, such as geographical constraints and accessibility issues. For students in remote areas, VR can provide access to resources and experiences that would otherwise be unavailable. Imagine a student living in a rural area being able to participate in a virtual field trip to a museum or historical site.
Additionally, VR can be particularly beneficial for students with special needs. Customized VR experiences can cater to individual learning requirements, providing tailored support that traditional classrooms may struggle to offer. For example, sensory-friendly environments can help students with autism engage in learning without overwhelming them.
Personalized Learning with VR
VR technology can be tailored to accommodate diverse learning styles, promoting inclusivity and engagement in the classroom.
By providing equal opportunities for all students, VR technology not only enhances learning outcomes but also promotes a more inclusive educational landscape. This ensures that every learner has the chance to thrive, regardless of their circumstances.
The Impact of VR on Memory Retention
Research in educational psychology suggests that experiential learning significantly enhances memory retention. VR's immersive nature allows students to engage with material actively rather than passively, which can lead to stronger memory formation. When learners are emotionally and physically engaged, they are more likely to remember what they've experienced.
For instance, studies show that students who participate in VR simulations tend to recall information better than those who learn through traditional lectures. The combination of visual, auditory, and kinesthetic input creates rich memories that are more easily accessed later. This multi-sensory approach also helps in forming connections between concepts, making learning more holistic.
Thus, integrating VR into educational settings can transform how students absorb and retain information, equipping them with knowledge that lasts well beyond the classroom.
Challenges and Limitations of VR in Education
Despite its many advantages, implementing VR in education is not without challenges. One major barrier is the cost associated with acquiring VR technology and developing quality content. Schools may struggle to allocate budgets for this kind of technology, which can hinder its widespread adoption.
Additionally, there can be a steep learning curve for both educators and students when integrating VR into the curriculum. Teachers may require professional development to effectively use VR tools, while students must adapt to a new mode of learning. Ensuring that both parties are comfortable with the technology is crucial for successful implementation.
Breaking Barriers to Education
VR can overcome geographical and accessibility challenges, offering equal learning opportunities for all students.
Lastly, while VR can provide engaging experiences, it should not replace traditional learning methods entirely. Striking a balance between VR and conventional teaching strategies ensures that students receive a well-rounded education that caters to various learning preferences.
Future Possibilities: VR and the Evolution of Learning
As VR technology continues to advance, its potential in education will only grow. Innovations such as improved graphics, haptic feedback, and more accessible devices will enhance the immersive experience, making learning even more engaging and effective. This evolution could revolutionize the way subjects are taught and learned, creating limitless possibilities for future generations.
Imagine a future where students can explore historical events or scientific concepts in a fully interactive virtual environment, collaborating with peers from around the world. Such experiences could foster global understanding and empathy, essential qualities in today’s interconnected society.

In conclusion, the intersection of VR technology and educational psychology holds incredible promise. By harnessing the power of immersive experiences, educators can create a more engaging, inclusive, and effective learning environment that prepares students for future challenges.